Recent Posts
Week 21 – Multiple high-severity vulnerabilities in VMware Cloud Foundation
19 – 15 May 2025 Multiple high-severity vulnerabilities were responsibly disclosed in VCF by Gustavo Bonito of the NATO Cyber Security Centre. From among these, our #CVEOfTheWeek is CVE-2025-41229. This is a Directory Traversal vulnerability, which might allow a malicious actor with network access to …
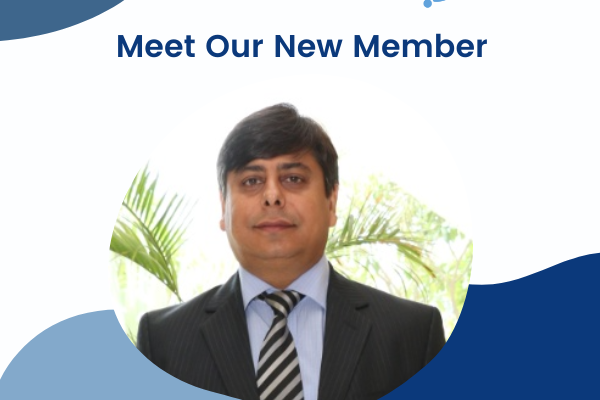
Welcome New Member – Sapann Talwar from Australia
Please welcome our newest member from Australia, Sapann Talwar Sapann is a seasoned Cybersecurity and Risk management practitioner with 26+ years of industry experience. He specializes in safeguarding ‘Data’ against evolving cyber threats and has a strong track record in developing and executing security strategies …
“What Happens to Heroes?” – Episode #5: The Unsung Heroes of the Digital World
The Psychological Impacts of Cyberattacks This is the fifth episode in our ongoing series about the individuals who, in a matter of moments, transition from employees to rescuers in the aftermath of a destructive cyberattack. These are what I call the “Heroes.” Let’s Rewrite the …